When it comes to designing user interfaces (UIs) for video games, the approach can vary significantly based on the genre of the game. Each genre has its unique requirements and player expectations, which can greatly influence how UIs are designed. In this article, we’ll explore UI strategies tailored for different game genres, focusing on RPGs (Role-Playing Games), FPSs (First-Person Shooters), and more.
1. UI Design for RPGs
Role-Playing Games (RPGs) often feature intricate worlds with deep narratives and complex gameplay systems. The UI in RPGs needs to support a rich array of features while ensuring that players can navigate and interact with the game world seamlessly.
Key Elements:
- Inventory Management: RPGs typically involve managing a wide array of items, from weapons and armor to potions and quest items. A well-designed inventory UI should be intuitive, allowing players to quickly access and organize their items. Incorporating drag-and-drop functionality and clear categorization can enhance usability.
- Character Status and Skills: RPG UIs often display detailed character stats, skills, and abilities. These elements should be presented in a clear and organized manner. Using progress bars, icons, and tooltips can help players easily understand their character’s status and abilities.
- Quest Logs and Maps: Given the complex narratives and numerous side quests in RPGs, providing a comprehensive quest log and an interactive map is crucial. The quest log should allow players to track active quests, view objectives, and access detailed information. Maps should be interactive, showing important locations and allowing players to set waypoints.
Example: The Elder Scrolls V: Skyrim features a well-organized inventory system with categories and sorting options, a detailed character status screen, and an interactive map with markers for quests and locations.
2. UI Design for FPSs
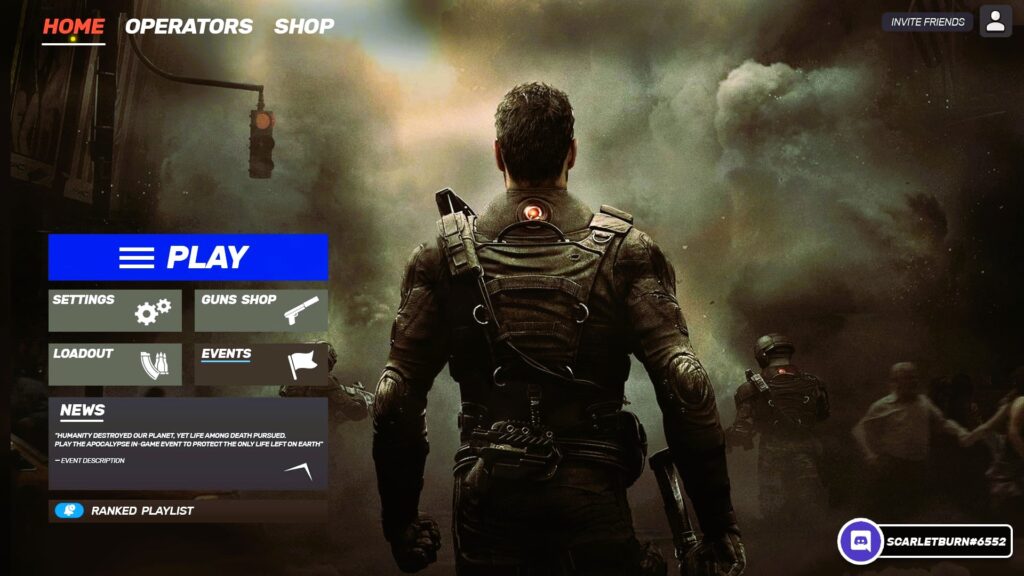
First-Person Shooters (FPSs) emphasize fast-paced action and precise control. The UI in FPS games needs to provide essential information without obstructing the player’s view or disrupting the immersion.
Key Elements:
- HUD (Heads-Up Display): The HUD is crucial in FPS games, as it displays essential information such as health, ammo count, and objective markers. The design should prioritize minimalism, ensuring that only critical information is shown and that it does not clutter the screen. Use transparent or semi-transparent elements to keep the focus on the action.
- Weapon Selection: Efficient weapon selection and management are key in FPS games. A quick-access weapon wheel or radial menu can streamline this process, allowing players to switch weapons quickly during combat.
- In-Game Notifications: FPS games often include in-game notifications for achievements, kills, or objectives. These notifications should be subtle yet noticeable, ensuring they provide valuable feedback without distracting from the gameplay.
Example: Call of Duty: Modern Warfare utilizes a clean HUD design with transparent elements for health and ammo, a radial weapon selection menu, and subtle notifications to keep players focused on the action. Did you like the article? Read also about Game UI Design.
3. UI Design for Strategy Games
Strategy games involve complex decision-making and resource management. The UI in strategy games needs to provide comprehensive information while facilitating strategic planning and execution.
Key Elements:
- Resource Management: Strategy games often involve managing resources such as currency, materials, or units. The UI should provide clear and concise information about resource levels and production status. Using graphs, bars, or counters can help players keep track of their resources effectively.
- Unit and Building Controls: Providing intuitive controls for unit selection and building construction is crucial. Grouping units, assigning commands, and managing building queues should be easily accessible. Contextual menus and shortcut keys can enhance efficiency.
- Strategic Overlays: Strategy games benefit from overlays that provide additional information about the game world. These overlays can include mini-maps, strategic layers, and information about enemy positions. They should be toggleable and non-intrusive, allowing players to access detailed information when needed.
Example: StarCraft II features a well-organized resource management system, intuitive unit and building controls, and strategic overlays that help players make informed decisions.
4. UI Design for Adventure Games
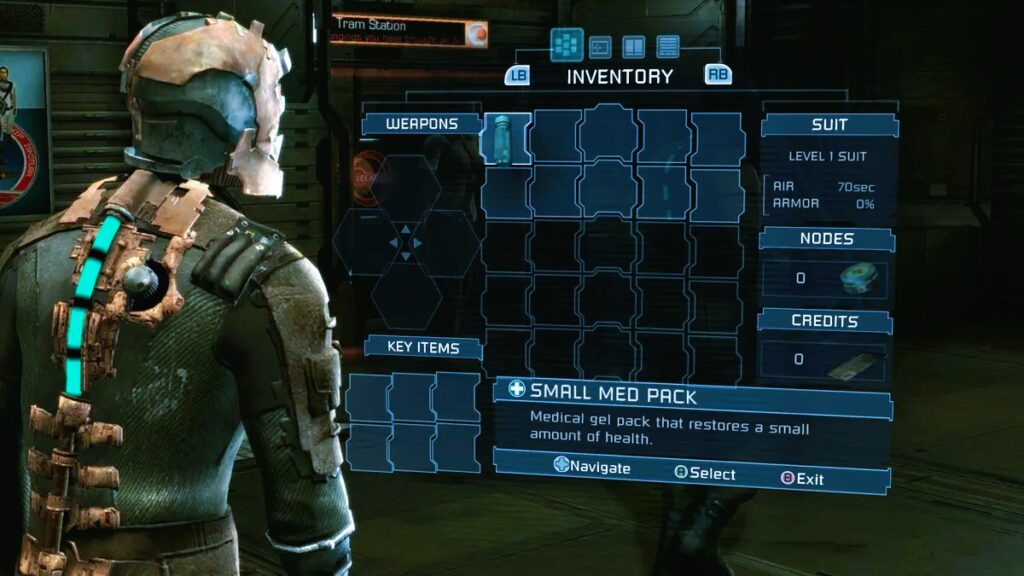
Adventure games often focus on exploration and puzzle-solving. The UI in adventure games should support these activities while enhancing immersion and narrative engagement.
Key Elements:
- Inventory and Puzzle Management: Adventure games often require players to manage items and solve puzzles. The inventory system should be easy to access and organize, with clear indications of item use. Puzzle elements should be integrated into the UI in a way that complements the gameplay.
- Narrative and Dialogue: Since adventure games emphasize storytelling, the UI should support dialogue and narrative elements effectively. This includes clear text boxes for conversations, choices, and narrative prompts.
- Exploration Aids: Providing aids for exploration, such as interactive maps or hints, can enhance the player’s experience. These aids should be optional and non-intrusive, allowing players to explore and discover at their own pace.
Example: The Legend of Zelda: Breath of the Wild features an intuitive inventory system, clear dialogue text boxes, and optional exploration aids such as the Sheikah Slate map and quest markers.
Designing UIs for different game genres requires a deep understanding of the gameplay mechanics and player expectations. Whether you’re designing for RPGs, FPSs, strategy games, or adventure games, it’s crucial to tailor the UI to enhance the overall player experience. By focusing on genre-specific elements and ensuring that the UI supports the gameplay effectively, you can create engaging and immersive interfaces that enhance the gaming experience.
For more insights into UI design standards and best practices, you can refer to resources such as Wikipedia’s Design Standards.