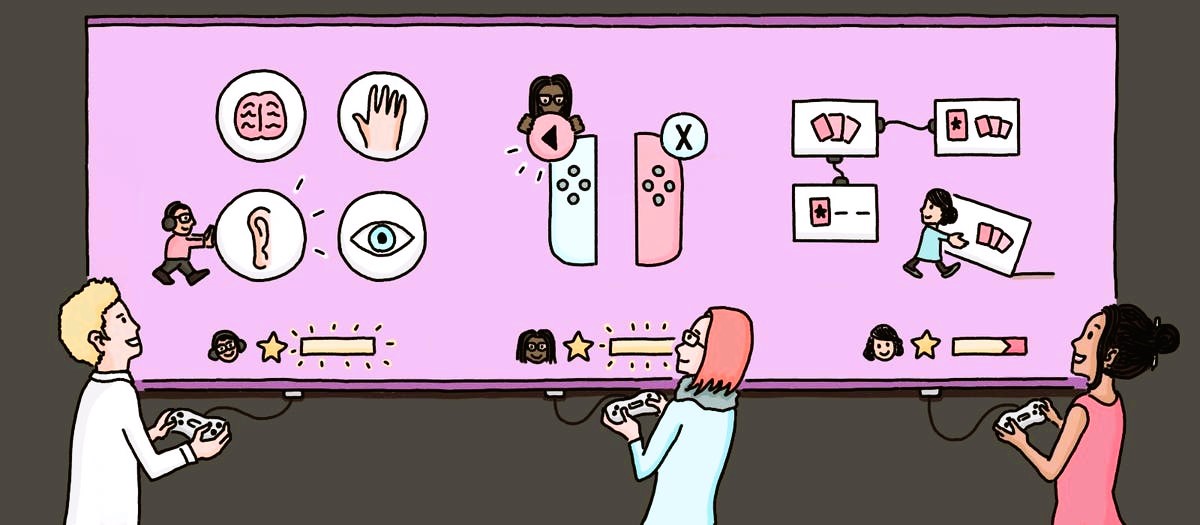
In game development, creating an engaging and functional User Interface (UI) is crucial to providing a positive player experience. Prototyping and testing are essential steps in the UI design process, allowing developers to refine their concepts and ensure they meet user needs. This article explores efficient methods for prototyping and testing game UI designs, offering practical tips and best practices to streamline the development process.
Understanding Prototyping and Testing
Prototyping and testing are iterative processes that help refine UI designs before they are finalized and implemented.
- Prototyping: Involves creating preliminary versions of the UI to visualize and experiment with design concepts. Prototypes can range from simple sketches to interactive mockups.
- Testing: Involves evaluating the prototypes to identify usability issues, gather feedback, and make improvements based on user interactions and preferences.
Steps to Efficient Prototyping
Effective prototyping allows designers to explore different UI concepts and iterate quickly. Follow these steps to streamline the prototyping process:
1. Define Objectives and Requirements
Before creating a prototype, clearly define the objectives and requirements for the UI. Consider the following:
- User Needs: Understand the needs and expectations of your target audience. What are their goals, preferences, and pain points?
- Game Context: Determine how the UI will fit within the overall game experience. What information and controls will players need, and how should they be presented?
2. Choose the Right Prototyping Tools
Selecting appropriate prototyping tools can significantly impact the efficiency of your design process. Consider these popular options:
- Wireframing Tools: Tools like Balsamiq or Adobe XD allow you to create basic wireframes that outline the layout and functionality of your UI.
- Interactive Prototyping Tools: Tools like Figma or Axure RP enable you to build interactive prototypes that simulate user interactions and transitions.
- Game Engines: For more advanced prototypes, consider using game engines like Unity or Unreal Engine, which allow you to create functional prototypes with integrated gameplay elements. Interactive menus and in-game interfaces, more details at this link.
3. Create Low-Fidelity Prototypes
Start with low-fidelity prototypes to quickly explore different design concepts. These can include:
- Sketches: Hand-drawn or digital sketches that outline the basic layout and functionality of the UI.
- Wireframes: Simple, static representations of the UI that focus on layout and structure without detailed graphics or interactions.
4. Develop High-Fidelity Prototypes
Once you have a solid concept, develop high-fidelity prototypes that include more detailed design elements:
- Visual Design: Incorporate colors, typography, and imagery that reflect the final look and feel of the UI.
- Interactive Elements: Add interactive components, such as buttons, sliders, and menus, to simulate user interactions and transitions.
Best Practices for UI Testing
Testing is crucial for identifying usability issues and ensuring that the UI meets player needs. Follow these best practices to conduct effective UI testing:
1. Conduct Usability Testing
Usability testing involves observing how players interact with the UI and identifying any difficulties or inefficiencies. Key aspects include:
- Task-Based Testing: Ask players to complete specific tasks using the UI, such as navigating menus or accessing features. Observe their interactions and note any issues or confusion.
- Think-Aloud Protocol: Encourage players to verbalize their thoughts while interacting with the UI. This can provide insights into their decision-making process and any difficulties they encounter.
2. Gather Feedback from Diverse Users
Collect feedback from a diverse group of users to ensure that the UI meets the needs of different players:
- Demographic Diversity: Test with players of varying ages, experience levels, and backgrounds to ensure that the UI is accessible and usable for all target audiences.
- Role-Based Testing: Include feedback from different roles, such as casual gamers, hardcore players, and game testers, to gather a range of perspectives.
3. Iterate Based on Feedback
Use the feedback gathered during testing to make informed improvements to the UI. Key steps include:
- Identify Common Issues: Look for patterns in the feedback to identify recurring issues or areas for improvement.
- Implement Changes: Make design adjustments based on the feedback, and create updated prototypes to test the changes.
- Retest: Conduct additional rounds of testing to verify that the changes address the identified issues and enhance the overall user experience.
Leveraging A/B Testing

A/B testing allows you to compare different versions of the UI to determine which performs better. Here’s how to implement A/B testing effectively:
1. Define Variables
Identify the specific elements or features you want to test, such as button placements, color schemes, or menu layouts. Create different versions (A and B) with variations in these elements.
2. Set Up Testing Scenarios
Implement the different UI versions within the game and expose them to different groups of players. Ensure that each group interacts with only one version of the UI.
3. Analyze Results
Gather data on player interactions, preferences, and performance for each version. Analyze the results to determine which version provides a better user experience and meets your design objectives.
Using Analytics and Metrics
Incorporate analytics and metrics to gain insights into how players interact with the UI and identify areas for improvement:
1. Track User Behavior
Use analytics tools to track user behavior, such as navigation patterns, click-through rates, and time spent on different UI elements. This data can help you understand how players use the UI and identify potential issues.
2. Monitor Performance Metrics
Track performance metrics, such as load times and responsiveness, to ensure that the UI functions smoothly and efficiently. Address any performance issues that may impact the player experience.
Efficient prototyping and testing are essential for creating effective game UI designs that enhance player experience. By defining objectives, choosing the right tools, and following best practices for prototyping and testing, developers can refine their UI concepts and ensure they meet user needs. Implementing A/B testing and leveraging analytics can further improve the design process and help create engaging and intuitive interfaces.
For more information on UI design standards and best practices, you can explore Wikipedia’s User Interface Design. This resource provides a comprehensive overview of UI design principles and guidelines, offering valuable insights for developers seeking to enhance their prototyping and testing processes.
By embracing these methods and techniques, game developers can create UI designs that not only meet player expectations but also contribute to a more enjoyable and immersive gaming experience.